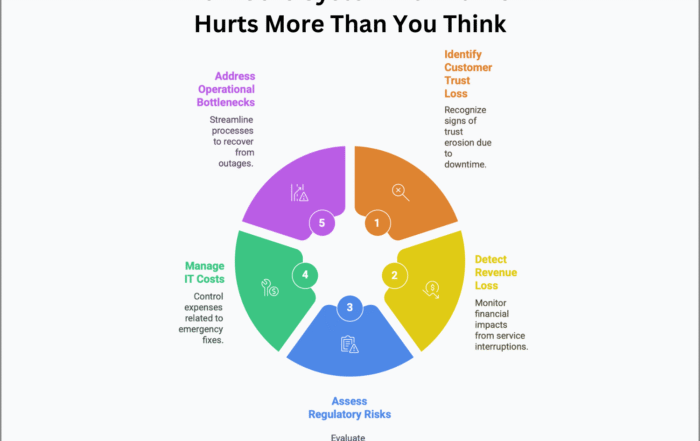
Emphasizing the critical role of comprehensive testing in core banking modernization to ensure system resilience, accuracy, security, and compliance, safeguarding against operational and regulatory risks.
In the intricate world of banking, where virtually every critical process rides on the backbone of core platforms – from origination to payments, lending to compliance – defect-free data and uninterrupted uptime are non-negotiable. Yet, complex core banking overhauls involving intricate integrations, migrations, and upgrades inherently heighten short-term technology risk profiles. Sensing potential exposures, regulators keep an increasingly watchful eye over transformational initiatives. In this environment, robust testing and quality assurance serve as the ultimate insurance policy, protecting core modernization programs by confirming everything works as intended before going live.
Importance of Testing New Core Banking Systems
Beyond simply verifying that new core solutions technically function in isolation, exhaustive testing regimes validate how fully aligned upstream and downstream dependencies will perform in concert. This is crucial for:
- Resilience: Stress testing against anomalous transaction volumes, processing failures, and more confirms continuity protections.
- Accuracy: Data validation ensures details flow properly across systems to prevent errors.
- Security: Penetration testing uncovers potential system access vulnerabilities.
- Compliance: Confirming controls alignment addresses oversight protocols.
With hundreds of interconnected technologies potentially impacted by core overhauls, testing provides the only way to reliably de-risk transitions from compromising critical operations.
Types of Core Banking Testing
Myriad testing types assess distinct aspects of technology reliability and resiliency:
- Functional Testing: Validates intended performance of routines and integrations.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Ensures usability for employees leveraging new solutions.
- Load/Volume Testing: Gauges system stability amid heavy workloads.
- Failover/Recovery Testing: Confirms continuity protections during outages.
- Data Migration Testing: Validates completeness and integrity of migrated information.
- Penetration Testing: Identifies potential security vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Testing: Confirms alignment with regulatory controls.
Tailoring testing regimes to align with specific modernization objectives and risk sensitivities ensures effective issue discovery and remediation.
Testing Best Practices
With so much at stake around core migrations, certain testing best practices prove invaluable:
- Iterative Testing Cycles: Conduct multiple testing rounds, revalidating areas subject to change after defects get uncovered and remediated with each successive cycle.
- Early Mock Migrations: Run simulation migrations in pre-prod to fix data flaws ahead of cutover events.
- Integrated Scenario Testing: Validate use cases involving multiple systems, not just individual platforms.
- Frequent Regression Testing: Confirm past fixes haven’t created new defects as updates get applied over time after launch.
Additionally, enlist internal bank users and partners to conduct user acceptance testing for added real-world validation.
The Cost of Skimping on Testing
Invariably conscious of budget and timeline pressures, some executives consider minimizing testing investments to accelerate launches or reduce expenses. This temptation must be resisted at all costs.
High-profile cases abound of major financial institutions rolling out defective core banking platforms and digital apps, requiring system shutdowns, processing workarounds, public scrutiny from regulators and customers, executive leadership fallout, and billions in remediation costs.
Cutting corners on quality assurance for core modernization to save pennies short-term threatens pounds long-term.
With so much at stake, new core banking systems warrant expansive testing lest defects cripple operations. Conducting iterative, integrated testing across functional, user acceptance, volume, security, compliance, and regression testing realms – while investing in continuous test automation – provides prudent protection. In the high-stakes world of banking, resilience and compliance are not mere buzzwords but essential safeguards for maintaining customer trust and regulatory adherence. Comprehensive testing is the linchpin that ensures core banking transformations deliver on their promises of operational excellence and future-readiness.
Found this article interesting? Check out these three related reads for more.
- Best practices for successful core banking system implementation
- Core banking system implementation challenges and success strategies
- Why is it referred to as a core banking transformation instead of just a migration?
#BankingQA #TestingCoreSystems