Ensuring seamless banking operations with Parallel Conversion: A meticulous approach to core banking transformation that balances innovation with risk management.
Have you ever felt like walking a tightrope without a safety net?
That’s how a core banking transformation can be without the right strategy. I recently spoke with a seasoned IT director who shared her experience steering a major banking transformation. Her team chose the Parallel Conversion approach, running both old and new systems side-by-side until they were confident the new one was foolproof. This method ensured their operations remained robust, providing a critical safety net that turned potential peril into a success story. But it wasn’t without the challenges.
What is Parallel Conversion?
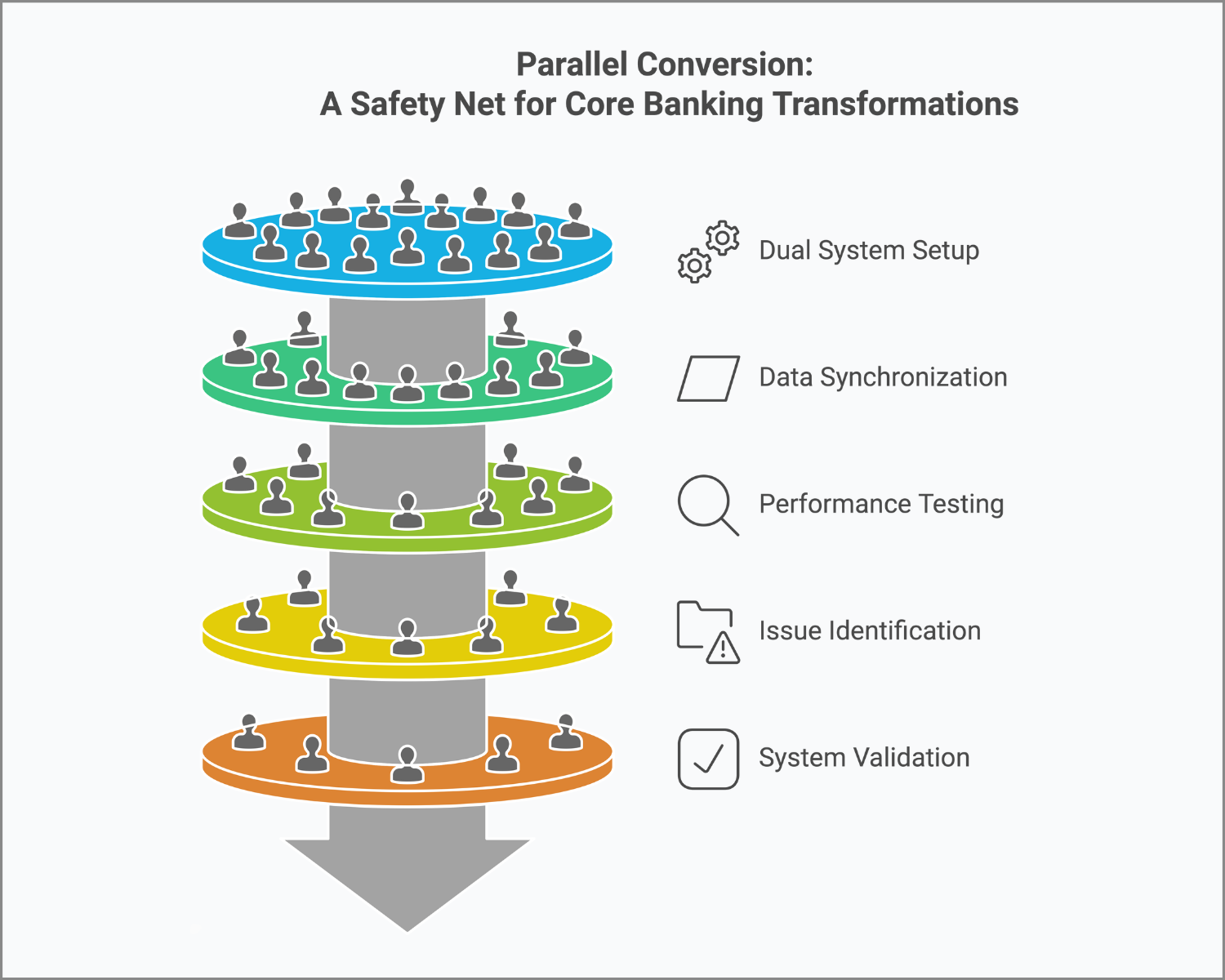
Parallel Conversion involves operating your existing core banking system alongside the new one for a set period. This dual-system approach acts as a real-time safety check, ensuring that every element of the new system functions perfectly before fully retiring the old one.
This method is ideal for banks where operational continuity is non-negotiable, such as in highly regulated environments where a single misstep could have far-reaching consequences. It’s like renovating your house while still living in it: inconvenient at times but safer and more pragmatic.
When to Consider Parallel Conversion
Parallel Conversion is best suited for scenarios where:
- Mission-Critical Operations: Banks that handle a high volume of transactions or sensitive data may prefer this method to ensure uninterrupted service.
- Risk Aversion: This strategy allows for thorough testing and validation and provides a fallback if the new system fails.
- Accuracy Needs: This is ideal for situations where data integrity and output accuracy are critical, as it allows for side-by-side output comparison.
- Complex Systems: Effective in environments with intricate legacy systems where phased integration might pose significant challenges.
- Risk Reduction: Provides an opportunity to catch issues before they affect the entire bank, minimizing operational risks.
- Validation and Testing: Allows actual performance comparisons between old and new systems under natural operational conditions.
- Business Continuity: Ensures that banking operations continue without interruption during the transition.
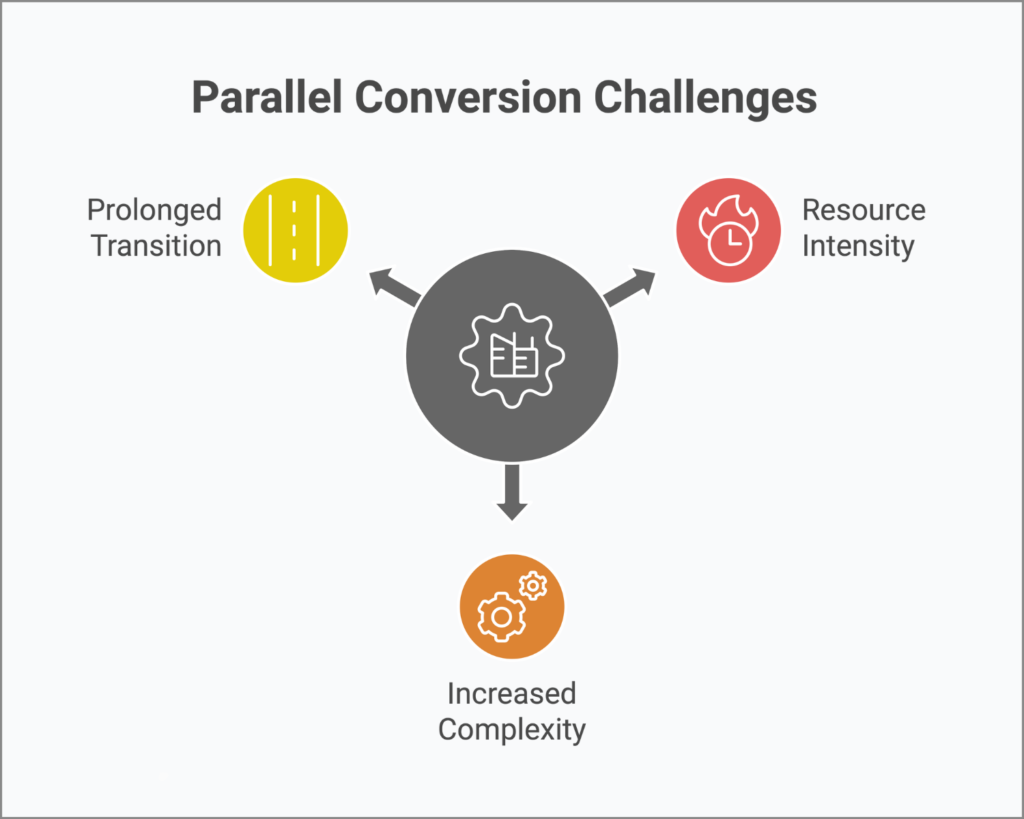
- Resource Intensity: Requires substantial resources and effort to run two systems concurrently.
- Increased Complexity: Managing two systems can complicate operations, requiring meticulous synchronization and oversight.
- Prolonged Transition: This might extend the overall timeline for completing the transformation, potentially delaying the realization of benefits from the new system.
- Define Clear Milestones: Establish specific criteria for successful validation. Decide how and when the transition from parallel to single-system operation will occur.
- Robust Data Management: Ensure impeccable data synchronization and integrity between the systems. Employ advanced tools to manage and monitor data flows seamlessly.
- Comprehensive Testing: Leverage the parallel period for exhaustive testing. Identify discrepancies and address them before completing migration.
- Effective Resource Allocation: Plan your resource use meticulously and ensure your team can manage the demands of operating dual systems.
- Stakeholder Communication: Keep all stakeholders informed about the transition process. Transparency helps manage expectations and facilitates smoother change management.
Advantages of Parallel Conversion
While resource-intensive, Parallel Conversion offers compelling benefits:
- Risk Reduction: Provides an opportunity to catch issues before they affect the entire bank, minimizing operational risks.
- Validation and Testing: Allows actual performance comparisons between old and new systems under natural operational conditions.
- Business Continuity: Ensures that banking operations continue without interruption during the transition.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its advantages, Parallel Conversion is not without challenges:
- Resource Intensity: Requires substantial resources and effort to run two systems concurrently.
- Increased Complexity: Managing two systems can complicate operations, requiring meticulous synchronization and oversight.
- Prolonged Transition: This might extend the overall timeline for completing the transformation, potentially delaying the realization of benefits from the new system.
Best Practices for Successful Parallel Conversion
To maximize the effectiveness of a Parallel Conversion, consider these strategies:
- Define Clear Milestones: Establish specific criteria for successful validation. Decide how and when the transition from parallel to single-system operation will occur.
- Robust Data Management: Ensure impeccable data synchronization and integrity between the systems. Employ advanced tools to manage and monitor data flows seamlessly.
- Comprehensive Testing: Leverage the parallel period for exhaustive testing. Identify discrepancies and address them before completing migration.
- Effective Resource Allocation: Plan your resource use meticulously and ensure your team can manage the demands of operating dual systems.
- Stakeholder Communication: Keep all stakeholders informed about the transition process. Transparency helps manage expectations and facilitates smoother change management.
When Dual Systems Provide Peace of Mind
For banks where downtime is not an option and the stakes are high, Parallel Conversion offers a controlled path to transformation. It allows financial institutions to test new waters while keeping their feet firmly planted in familiar territory.
Imagine managing a transformation where you can test every scenario before going live—Parallel Conversion offers that possibility, providing both peace of mind and a strategic advantage.
Choosing Parallel Conversion means opting for a meticulous, measured approach to system transformation. It’s about prioritizing operational security and precision over speed. If your bank values certainty and thoroughness, this method could offer the most practical route to modernization.
Ready to Explore More?
If you’re interested in learning more about phased conversions and other transformation strategies, head over to our Execution Strategies Hub for comprehensive insights. Don’t forget to check out our Main Infographic for a visual breakdown of each approach. Continue your journey with the Next Spoke Article #4, which dives into another crucial execution method. You can also visit our Conversion Strategies Hub to get a complete overview of all available paths for your core banking transformation. Equip yourself with the knowledge to make the best decision for your bank’s future.
#CoreBankingTransformation #ExecutionStrategy